We’ve put together a comprehensive guide explaining what polycarbonate sheeting is and all its uses, ensuring on your next project, you will know what materials are needed and how the sheeting can be used to help.
Topics covered include:
- What polycarbonate is
- How it is made
- Different types
- Characteristics
- What is polycarbonate sheeting?
- What can it be used for?
- Different types of sheeting for roofing
- Advantages of the lightweight material
- Acrylic vs Polycarbonate
What is polycarbonate?
So, let’s start with polycarbonate itself. According to the Oxford Dictionary, the definition is “A synthetic resin in which the polymer units are linked through carbonate groups, including many moulding materials and films.”
To put it simply, polycarbonates are strong, stiff, hard, tough, transparent engineering thermoplastics that are known for being mouldable, durable and lightweight. This makes it one of the most widely used engineering thermoplastics.
It was first discovered in 1898, by a German scientist called Alfred Einhorn who was working at the University of Munich, however, it wasn’t commercialised until the 1950s and instead of being glass clear like it is now, it had a brownish tint up until 1970.
According to a global forecast by marketsandmarkets.com the thermoplastic sheets market was valued at USD 1.61 Billion in 2017 and is projected to reach USD 2.11 Billion by 2023 at a compound annual growth rate of 4.5%. This is partly thanks to polycarbonate roofing becoming more popular, replacing glass, acrylic, and other similar materials thanks to its ease of installation, durability, the passage of safe light, excellent insulation, aesthetic appeal and availability of different varieties.
How is polycarbonate made?
According to British Plastics Federation (BPF), polycarbonate is most commonly formed with the reaction of bisphenol A, which is produced through the condensation of phenol with acetone under acidic conditions, with carbonyl chloride in an interfacial process. The structural strength of is due to the covalent bonds which exist between all these elements. It falls into the polyester family of plastics.
It is available in a number of different grades depending on the application and processing method. These different grades are used in a range of our products. Flame retardant grade polycarbonate is used in our Blizzard Hygiene Cladding whilst reinforced and stress crack resistant grade polycarbonate is used in our Stratus Flat Sheeting.
Through extrusion, it can be formed into different profiles with uniform cross-section or continuous length. Such products can be used for roofing applications. In most cases, this process can be categorised as a solid sheet, multiwall sheet and profile extrusion.
What are the different types of polycarbonate?
The variety of ways polycarbonate can be created is virtually limitless thanks to its flexible nature.Just a few of the different types include:
- Clear
- Abrasion-Resistant
- Mirrored
- Anti Static
- Bulletproof
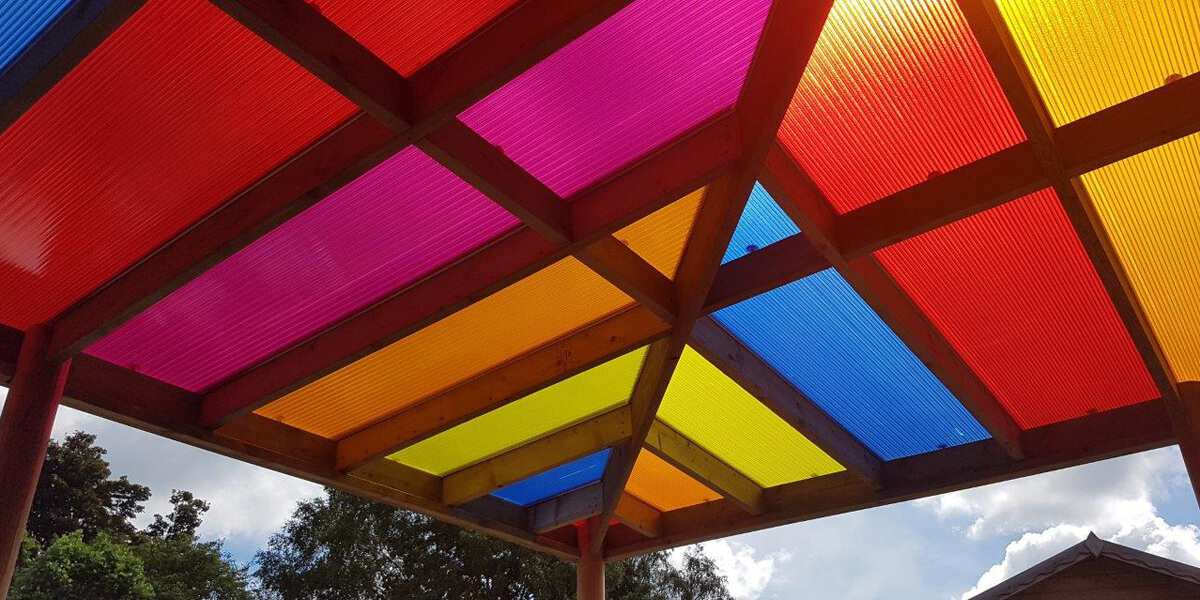
- Coloured/Tinted
What are the characteristics of polycarbonate?
Polycarbonates can maintain rigidity up to 140°C and toughness down to -20°C or, with special grades, even lower. The material is amorphous, therefore it displays excellent mechanical properties and high dimensional stability. It’s heat resistant up to 135°C and rated as slow-burning, plus special flame retardant grades exist, which pass several severe flammability tests. Our BLIZZARD Hygiene Cladding has a class one fire rating, protecting your surface from the spread of flames and high temperatures.
Polycarbonate possesses impact resistance 250 times greater than that of glass while also exhibiting exceptional tensile strength. It doesn’t have to be clear, it can be tinted and coloured, or even made to reflect like a glass mirror, which thanks to polycarbonates’ high impact strength (up to 250 times greater than that of glass!), makes it perfect for destructive environments. It can even be made to be bulletproof, and in this case, is often referred to as ‘bulletproof glass’.
One of the downsides of the transparent sheeting is that it’s more susceptible to scratching than glass, however, there are abrasive resistant forms of polycarbonate that are specifically designed to address this and give it high abrasion resistance.
Some polycarbonate is made anti-static by coating it with a metal and plastic mixture that prevents the generation of static electricity and can provide excellent chemical resistance. STORMClad a PVC sheet, offers excellent resistance to chemicals and can be used in food and hygiene areas, clinics, hospitals, schools, laboratories and commercial kitchens.
Polycarbonate is fully recyclable and provides an excellent yield for plastic recycling facilities. The usual process for recycling it is to sort, shred, wash, granulate and then compound ready for re-use. This is because, according to Creative Mechanisms, thermoplastic materials become liquid at their melting point, then they can be cooled, and reheated again without significant degradation, allowing them to be easily injection moulded and recycled. Whereas thermoset plastics can only be heated once. If you tried to heat them a second time it would simply burn.
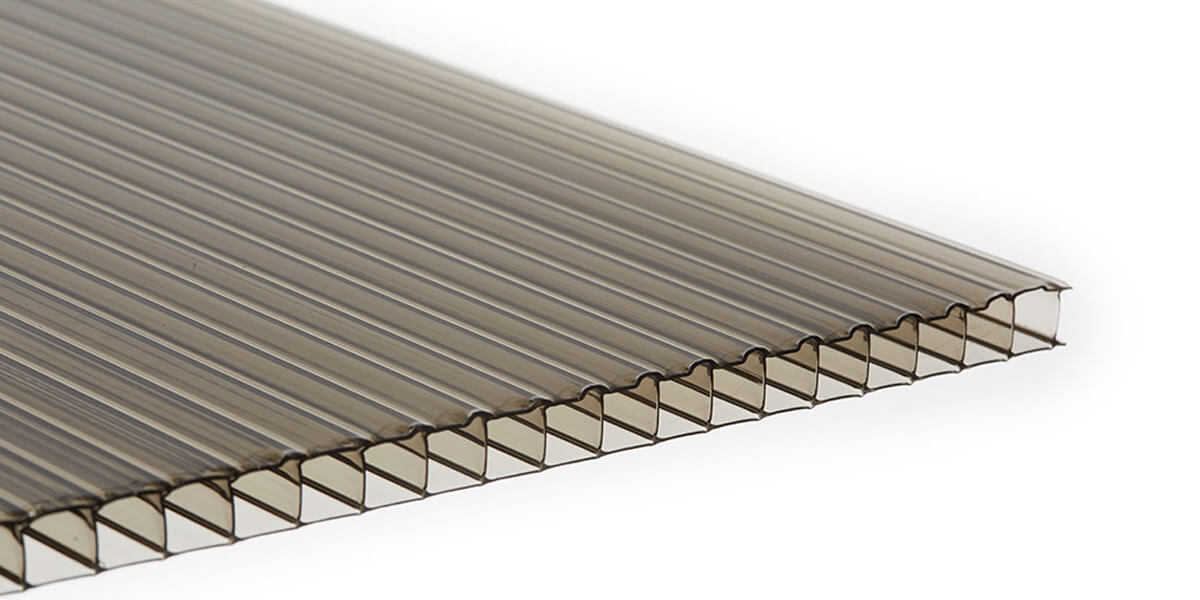
What is polycarbonate sheeting?
Polycarbonate sheeting is typically polycarbonate that has been formed into a sheet via injection moulding, structural foam moulding, extrusion, vacuum forming or blow moulding.
What can polycarbonate sheeting be used for?
Thanks to its durability, weight and flexibility, polycarbonate is incredibly versatile and is used in a variety of markets, most noticeably in the automotive, glazing, electronic, business machine, optical media, medical, lighting and appliance markets.
Polycarbonate sheeting has almost unlimited applications, here are just a few:
- Conservatories
- Canopies
- Vertical glazing
- Displays
- Curved and Industrial Rooflights
- Signage
- Covered Walkways
- Swimming Pool Covers
- Insulation
- Power Distribution
- Connectors
- Mobile Phones
- Vehicle Dashboards
- Cladding
- Power Tools
- Baby Bottles
- Gym Mirrors
- Riot Shields
- Water Dispensers
- Garden Equipment
- Medical Applications
- Sporting Goods
- Train Windows
- Bus Shelters
- Traffic Lights
What are the different types of polycarbonate roof systems?
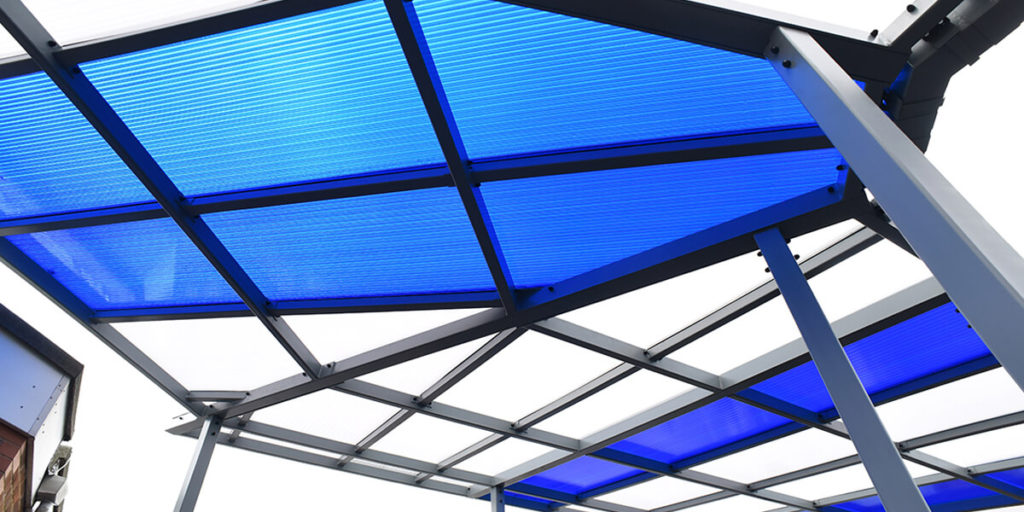
In regards to building, specifically roofing, polycarbonate sheeting comes in the form of twin-wall, multiwall, solid and corrugated sheets.
Twinwall and multiwall polycarbonate sheets are the most widely used form of thermoplastics, often used for conservatories and lean-to roofs. Ideal for conservatories, canopies, vertical glazing, displays, roof lights, signage, walkways, swimming pool covers, insulation and more.
Solid polycarbonate sheets are thick for a solid and virtually unbreakable roofing system. This is ideal for protective screens, vertical glazing, bus shelters, windows and doors, train windows and riot shields. Solid Polycarbonate sheets deliver the transparency of glass, are UV protected on both faces and are ideal for skylights, helmets, security glazing, balustrades, balconies and more.
Corrugated polycarbonate sheets can be bent or folded into your desired design and can be layered on top of other sheets making it easier to fit the pieces of roofing sheets. These can be used for conservatories, signage, roofing, glazing, DIY, swimming pools, greenhouses and more.
What are the advantages of polycarbonate sheeting?
Polycarbonate sheeting can provide abrasion resistance, chemical protection, strength and impact resistance, UV protection, heat and flammability resistance, workability, transparency, and it’s recyclable.
The various layers that multiwall polycarbonate sheeting is made up from provides superb thermal insulation, as well as relatively good sound insulation.
Our FORCE range of polycarbonate sheeting is co-extruded with a UV protection layer, offers high levels of impact resistance, outstanding strength to weight ratio, superior insulation, high optical clarity, and is energy-saving, lightweight and easy to handle.
On special request, we can provide coloured sheeting, ideal for school canopies.
Acrylic vs polycarbonate
Polycarbonate and acrylic both boast impressive levels of damage resistance, however generally speaking polycarbonate are consistently stronger than acrylic, as it boasts much higher levels of impact resistance. Polycarbonate can also be safely drilled anywhere on the sheet with a standard bit and suffers no damage, whereas acrylic becomes more and more likely to break when drilling closer to the corners.
STORM Building Products offer an extensive range of polycarbonate sheeting and other building plastics, supplying one of the most comprehensive ranges of superior quality building products in the UK. Delivering high-quality materials, including polycarbonate cladding and roof systems, at competitive pricing and outstanding customer service with brand integrity sets STORM apart.
Call us today on 01278 455326 or email your enquiry to [email protected] to discuss your requirements or request a catalogue.
This article was written by Jade Mitchell,
Jade is the Marketing Coordinator at STORM Building Products, she has been working in the building plastics industry since 2016 and has completed ISMM level 2 and 3.